A collection of powerful monophonic and polyphonic synthesisers in 'Blocks' format.

Details:
The synths feature versatile internal modulations and are designed to be integrated with the other packs for expanded modulation and effects routing. The bundle includes a sophisticated Piano Roll block with extensive editing and modulation functions and a suite of polyphonic utility and modulation blocks to augment and expand the polyphonic functionalities of the synths.
Polyphonic Ports:
The polyphonic blocks feature special polyphonic ports denoted by a light grey circle around the edge of the port.
Polyphonic output ports can be connected to monophonic input ports and vice versa. There are also various utility blocks to convert polyphonic output signals to monophonic signals, for example the polyphonic mixer has a monophonic output that can be used to mix polyphonic voices down to a monophonic signal.
Monophonic output ports can be connected to polyphonic input ports, so you can for example connect a monophonic signal from the free pack oscillator to the polyphonic A&B modulation input ports of the Polyphonic Mini Synth.
All polyphonic blocks are set to 5 note polyphony by default. The polyphony can be increased by increasing the blocks' polyphony setting in the inspector when the blocks are loaded in ensemble mode.
(Note: there is no overlap between the Synth Bundle and the Blocks Bundle, all included blocks are exclusive to this bundle.)
Included modules:
Synths
- FM Synth
- Quad Synth
- Dual Synth
- Mini Synth
- Supersaw Synth
- Multi-Breakpoint Synth
- Granular Sample Player (Polyphonic)
- Sample Player (Polyphonic)
- Sampler (Polyphonic)
- Sampler (Stereo Polyphonic)
- Dual Synth (Polyphonic)
- FM Synth (Polyphonic)
- Mini Synth (Polyphonic)
- Multi-Breakpoint Synth (Polyphonic)
- Piano (Polyphonic).ism
- Quad Synth (Polyphonic)
- Supersaw Synth (Polyphonic)
Oscillators
- Multi Oscillator (Polyphonic)
- Oscillator (Polyphonic)
- Quad Oscillator (Polyphonic)
- Wavetable (Polyphonic)
- Wavetable Basic (Polyphonic)
Filters
- Comb Notch Filter (Polyphonic)
- Filter (Polyphonic)
- Mini Filter (Polyphonic)
Modulation
- Envelope (Polyphonic)
- Envelope (Stereo Polyphonic)
- Multi-Breakpoint Envelope (Polyphonic)
- Randomizer (Polyphonic)
Effects
- Unison (Polyphonic)
- Real Verb
- Box Verb
Sequencers
- Piano Roll
Utilities
- 4 Ch Mixer (Polyphonic)
- Dual VCA Mixer (Polyphonic)
- Mono Note Merge (Polyphonic)
- Mono To Voice
- Multiply (Polyphonic)
- Note To Gate
- Poly Note Merge (Polyphonic)
- Poly To Mono
- Poly Voice Split
- Short Delay (Polyphonic)
- Sum (Polyphonic)
- Util Note In (Polyphonic).ism
- Chord Bank (Polyphonic)
- Clock Multiplier
- Gate Probability
- Quantize
- Sequential Switch
- Split
- Split (Polyphonic)
- Transpose (Polyphonic)
- Voice Split
- Keyboard
- MIDI Out (Polyphonic)
- Mono Note Merge (Polyphonic)
- Mutes X8
- Note Delay (Polyphonic)
- Note In (Polyphonic)
- Gate Merge
FM Synth
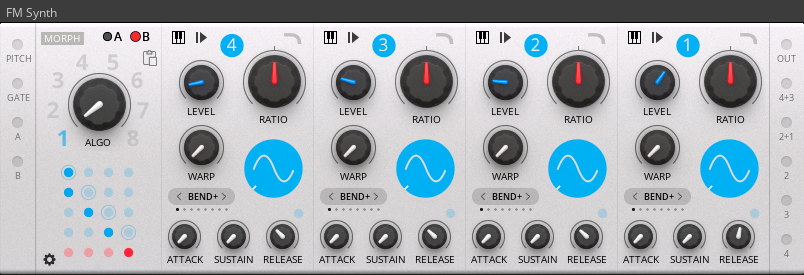
A 4-Operator (4 oscillator) FM Synth.
Each of the 4 oscillators features a 'Warp' control that bends the waveform in 8 ways:
- BEND+ = Bends the waveform to one side.
- BEND- = Bends the waveform out towards the edges.
- ASYM (Asymmetry) = Squishes the waveform from the middle to the edge in a linear fashion for 'Pulse Width Modulation' style effects.
- SYNC = Duplicates the the waveform a number of times, simulating the 'sync' function found on older analogue synthesisers.
- HYPER = Warps the waveform in an aggressive fashion.
- FOLD (wave-folding) = The waveform acts like a wave-shaper to transform a sine wave. Can be used to create very bright / complex sounds with lots of harmonics.
- WRAP = The waveform is stretched vertically and wrapped back down creating multiple jagged folds.
- RAND = Generates random values (noise). The 'WARP' control sets the transition slope between values (fully anticlockwise = stepped transitions). The random signal output is 'shaped' according to the setting of the 'WAVE' control. The 'COARSE / FREQ / LENGTH' knob sets the frequency of the randomly generated values. With these controls a wide selection of random signals and colours of noise can be generated. Set 'SYNCHRONISATION MODE' to 'FREE' and the 'FREQ' knob to maximum to generate white noise.
The 4 oscillators also have 3 synchronisation modes:
- FREE (wave icon) = The pitch of the oscillator can be set freely with no synchronisation.
- KEY TRACK (keyboard icon) = You can control the pitch of the oscillator via the Pitch input.
- CLOCK (clock Icon) = The speed of the oscillator is synchronised with the master tempo.
FM Routing Matrix
The FM algorithms are defined using a 4x4 FM routing matrix (blue LEDs) with 4 separate values for output levels (red LEDs). The circled blue LEDs indicate a feedback path (the oscillator modulating itself). The FM matrix works in a similar way to the 6x6 FM matrix found in the FM7/FM8 soft-synth.
The FM modulation signals flow down from the top of the matrix in the following order:

And connect to the FM inputs of the oscillators by leaving to the side of the matrix in the following order:

If you imagine the circled LEDs represent each operator of the algorithm (operator means 'oscillator' in FM terminology), from operator 4 at the top left to operator 1 at the bottom right, then it's easy to visualise the connections between each of the operators.

The LEDs below the circled LEDs indicate connections from higher numbered operators to lower numbered operators, for example operator 2 modulating operator 1:

The LEDs above the circled LEDs indicate connections from lower numbered operators to higher numbered operators, for example operator 2 modulating operator 3. Operator 3 can then be heard at the output by turning up the red LED below it:

Turning up the circled LEDs will modulate the operator by itself, operator feedback is generally used in FM algorithms to give the operator a brighter or noisier sound:

Different algorithms can be stored in 8 presets and the values of the FM routing matrix for each algorithm preset can edited by dragging up and down on the LEDs.
The algorithm presets can be recalled with the 'ALGO' knob or via modulation (up to audio rate). When 'Morph' mode is enable the values are smoothly interpolated between algorithms. The algorithms can be selected for editing by turning the knob or clicking on one of the numbers.
Each oscillator has it's own envelope which controls the level of the oscillator before it enters the FM matrix. The envelopes can be looped and used as additional LFOs or can even be set to loop at audio frequencies and used as additional oscillators. The envelopes can also be used as a modulation source using the internal modulation routing controls described below.
Internal Modulation Routing
There are controls on the 'Options Page' (cog icon) that allow a number of modulation sources to be routed to the internal A & B modulation busses for each oscillator in the synth:

Sources includes all 4 envelopes (envelopes 4 & 3 are connected to the upper control and envelopes 2 & 1 to the lower control), the 4 oscillators, a built in LFO, velocity and pitch. If 'EXT' is selected then the A & B ports are used for the modulation busses for that oscillator. For convenience if no cables are connected to either the A or B input ports then Modulation Bus A will be connected to that oscillator's envelope by default and Modulation Bus B will be connected to the built-in global LFO.
Pitch Snap Mode
There are 3 modes of operation for the coarse pitch knobs for each oscillator
- OFF = The coarse pitch knob is not snapped and changes the frequency freely.
- EVEN = The coarse pitch knob is snapped to even, semitone intervals
- RATIO = The coarse pitch knob is snapped to the closest FM ratios (1:1, 9:8, 5:4 etc). The ratios are displayed below the knob.
Low Pass Gate
Each oscillator features it's own low pass gate (a low pass filter controlled by the envelope). This is useful for filtering out higher frequencies generated by more extreme FM settings. The low pass gate for each oscillator is enabled by clicking on the 'Low Pass' icon at the top of each oscillator's panel.
Quad Synth
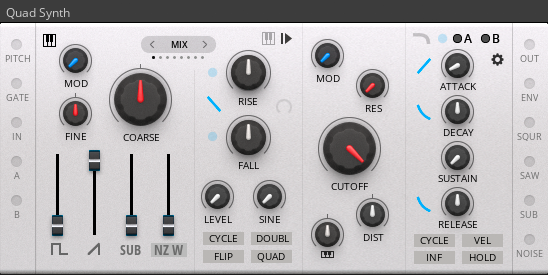
A synth that combines a four-waveform oscillator, a 'ramps' modulation section, a filter and an envelope that can also function as a 'Low Pass Gate'.
The oscillator is based on a detailed sampling of a famous polyphonic hardware synth from the 1980s. The samples have been carefully recorded and matched to maintain perfect phase relationships between the 4 oscillators resulting in a very authentic sound.
The modulation section is based on the 'Ramps' module from the designers pack (see designers pack for more details).
The filter section is based on the 'Squelch' Filter from the designers pack which is modelled on another famous hardware synth from the 1980s (see designers pack for more details).
Dual Synth

A versatile synth that combines 2 separate oscillators, a mixer section that can combine and mix the 2 oscillators in a variety of ways and an envelope section that can also function as a 'Low Pass Gate' (LPG).
Each of the 2 oscillators features a 'Warp' control that bends the waveform in 8 ways:
- BEND+ = Bends the waveform to one side.
- BEND- = Bends the waveform out towards the edges.
- ASYM (Asymmetry) = Squishes the waveform from the middle to the edge in a linear fashion for 'Pulse Width Modulation' style effects.
- SYNC = Duplicates the the waveform a number of times, simulating the 'sync' function found on older analogue synthesisers.
- HYPER = Warps the waveform in an aggressive fashion.
- FOLD (wave-folding) = The waveform acts like a wave-shaper to transform a sine wave. Can be used to create very bright / complex sounds with lots of harmonics.
- WRAP = The waveform is stretched vertically and wrapped back down creating multiple jagged folds.
- RAND = Generates random values (noise). The 'WARP' control sets the transition slope between values (fully anticlockwise = stepped transitions). The random signal output is 'shaped' according to the setting of the 'WAVE' control. The 'COARSE / FREQ / LENGTH' knob sets the frequency of the randomly generated values. With these controls a wide selection of random signals and colours of noise can be generated. Set 'SYNCHRONISATION MODE' to 'FREE' and the 'FREQ' knob to maximum to generate white noise.
The 2 oscillators also have 3 synchronisation modes:
- FREE (wave icon) = The pitch of the oscillator can be set freely with no synchronisation.
- KEY TRACK (keyboard icon) = You can control the pitch of the oscillator via the Pitch input.
- CLOCK (clock Icon) = The speed of the oscillator is synchronised with the master tempo.
The mixer section has 8 modes with which it uses to mix the 2 oscillators:
- MIX = Normal Mixer.
- RING A = Analog Ring Modulation.
- RING D = Digital Ring Modulation.
- AM A = Analog Amplitude Modulation.
- AM D = Digital Amplitude Modulation.
- S&H = Sample & Hold Method 1 (Hold when modulating signal crosses zero).
- HOLD = Sample & Hold Method 2 (Hold when modulating signal is positive, pass when modulating signal is negative).
- OR = Selects the signal with the most positive amplitude.
Mini Synth

A compact single oscillator synth with a built in envelope and a low pass gate (LPG).
The oscillator features a 'Warp' control that bends the waveform in 8 ways:
- BEND+ = Bends the waveform to one side.
- BEND- = Bends the waveform out towards the edges.
- ASYM (Asymmetry) = Squishes the waveform from the middle to the edge in a linear fashion for 'Pulse Width Modulation' style effects.
- SYNC = Duplicates the the waveform a number of times, simulating the 'sync' function found on older analogue synthesisers.
- HYPER = Warps the waveform in an aggressive fashion.
- FOLD (wave-folding) = The waveform acts like a wave-shaper to transform a sine wave. Can be used to create very bright / complex sounds with lots of harmonics.
- WRAP = The waveform is stretched vertically and wrapped back down creating multiple jagged folds.
- RAND = Generates random values (noise). The 'WARP' control sets the transition slope between values (fully anticlockwise = stepped transitions). The random signal output is 'shaped' according to the setting of the 'WAVE' control. The 'COARSE / FREQ / LENGTH' knob sets the frequency of the randomly generated values. With these controls a wide selection of random signals and colours of noise can be generated. Set 'SYNCHRONISATION MODE' to 'FREE' and the 'FREQ' knob to maximum to generate white noise.
The oscillator also has 3 synchronisation modes:
- FREE (wave icon) = The pitch of the oscillator can be set freely with no synchronisation.
- KEY TRACK (keyboard icon) = You can control the pitch of the oscillator via the Pitch input.
- CLOCK (clock Icon) = The speed of the oscillator is synchronised with the master tempo.
Internal Modulation Routing
There are controls on the 'Options Page' (cog icon) that allow a number of modulation sources to be routed to the internal modulation busses:

Sources includes the envelope, a built in LFO, velocity and pitch. If 'EXT' is selected then the A & B ports are used for the modulation busses. For convenience if no cables are connected to either the A or B input ports then modulation bus A will be connected to the envelope by default and modulation bus B will be connected to the built-in LFO.
Low Pass Gate
The oscillator features a built-in low pass gate (a low pass filter controlled by the envelope). The low pass gate is enabled by clicking on the 'Low Pass' icon at the top of the panel.
Supersaw Synth

A simple synth based on a single supersaw oscillator. The oscillator engine runs in 12bits and the sample rate can also be reduced for a gritty old-school supersaw sound. The 'CHORD' control sets the note interval between the unison voices, a variety of chords and intervals can be selected. When 'SCALE SNAP' is enabled the notes in the chord are snapped to a scale (use the coarse transpose control to set the key).
Internal Modulation Routing
There are controls on the 'Options Page' (cog icon) that allow a number of modulation sources to be routed to the internal modulation busses:

Sources includes the envelope, a built in LFO, velocity and pitch. If 'EXT' is selected then the A & B ports are used for the modulation busses. For convenience if no cables are connected to either the A or B input ports then modulation bus A will be connected to the envelope by default and modulation bus B will be connected to the built-in LFO.
Low Pass Gate
The oscillator features a built-in low pass gate (a low pass filter controlled by the envelope). The low pass gate is enabled by clicking on the 'Low Pass' icon at the top of the panel.
Multi-Breakpoint Synth

A synth that combines a multi-breakpoint oscillator, a sub oscillator, a RAMPS section, a filter and an envelope that can also function as a 'Low Pass Gate'. The synth features versatile modulation and routing options between the sections.
Granular Sample Player (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic granular sample player. The granular sampler player reads small chunks of the sample (grains) at the playback position and then plays back the sample in any direction as a dispersed cloud of grains.
A ‘Scan’ function scans the playback position through the sample in order to play it back. The scanner's start position, length of playback and speed of playback are set by the ‘START’, ‘LENGTH’ and ‘SPEED’ controls. There are 6 playback modes for the ‘Scan’ function:
- LOOP = The position is scanned in one direction, continuously looping.
- PONG (ping-pong) = The position is scanned in one direction and then reverses, continuously looping forwards and then backwards in a ping-pong fashion.
- ONCE = The position is scanned in one direction and then stops when it reaches the end of its scan.
- END = The position is scanned in one direction and then loops only the end part of the scan. This is useful for scanning through samples of real instruments so that the beginning / attack portion of the sample only plays once and then only the sustain portion is looped.
- RAND (random) = Randomly scans through the sample.
- TRACK (key tracking) = The speed of the scan is controlled by the pitch input port. With this mode enabled reduce grain length and change the 'COURSE' tuning for formant style effects.
- TRACK L (key tracking + looping) = Same as TRACK mode except looping.
There are 7 controls on the ‘Options’ page to change the settings of the granular engine. The settings are for grain length, grain density, grain cross fade and 4 jitter controls (random fluctuations) for position, pitch, length and density.
The Granular Sample Player has no built-in samples, drag and drop a sample file to load it. Use the ‘SELECT’ control to select which of the loaded sample files is being used. As well as being able to drag and drop sample files you can also load samples into Reaktor's built in sample map editor where you can specify velocity layers and set up complex multi-sample maps. You can also embed the sample files into the block.
When the ‘MAP’ button (small keyboard icon) is enabled the samples are mapped across the keyboard and selected by the pitch input.
Waveform Display: the dark blue area shows the area of the sample played by the playback scanner, the light blue area shows the area of the sample that the grains are currently being read from, the white line shows the start position and the light grey line shows the playback position.
Sample Player (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic sample player. Drag and drop a sample file load it. Use the ‘SELECT’ control to select which of the loaded sample files is being used. As well as being able to drag and drop sample files you can also load samples into Reaktor’s built in sample map editor which will allow you to embed the files into the block.
Drag and drop a sample file to load it. Use the ‘SELECT’ control to select which of the loaded sample files is being used. As well as being able to drag and drop sample files you can also load samples into Reaktor's built in sample map editor where you can specify velocity layers and set up complex multi-sample maps. You can also embed the sample files into the block.
The sampler player features a ROUND-ROBIN mode, when enabled the sample player cycles through the loaded samples with every gate received at the gate input.
When the ‘MAP’ button (small keyboard icon) is enabled the samples are mapped across the keyboard and selected by the pitch input.
The 'FM MODE' control selects one of 5 FM Modes:
- FREQ = The FM input modulates the pitch of the sample, the FM knob sets the amount of modulation.
- PHASE = The FM input modulates the phase (playback position) of the sample, the FM knob sets the amount of modulation.
- PHASE 2 = Same as PHASE 1 but the FM input signal is offset.
- SCRATCH = The FM knob plays through the sample like a record being scratched, the FM input is ignored.
- DIRECT DRIVE = The value of the FM input, between 0 and 1, offsets the playback position across the whole length of the sample, the FM knob sets the amount of offset.
Sampler (Stereo Polyphonic)

A polyphonic sampler block that has the ability to record audio from its input port (like a real hardware sampler). The sampler can record into the buffer and playback from the buffer simultaneously. Waveform Display: the white line shows the start position, the light grey line shows the playback position and the red line shows the record position.
Recording can be set to loop around the buffer continuously or stop recording when it gets to the end of the buffer. Recording can be restarted using the 'REC' input port or if the sampler is first put into 'ARM' mode then recording can be restarted when the audio level exceeds a threshold or restarted by the 'RESET' port (similar to a how 'arm' mode works on hardware sampler). The 'ARM', 'REC' and 'PLAY' controls can also be controlled via the A/B modulation inputs.
The contents of the buffer is stored with patches and snapshots. Sample files can also be drag and dropped onto the waveform display to load them into the buffer.
The 'FM MODE' control selects one of 5 FM Modes:
- FREQ = The FM input modulates the pitch of the sample, the FM knob sets the amount of modulation.
- PHASE = The FM input modulates the phase (playback position) of the sample, the FM knob sets the amount of modulation.
- PHASE 2 = Same as PHASE 1 but the FM input signal is offset.
- SCRATCH = The FM knob plays through the sample like a record being scratched, the FM input is ignored.
- DIRECT DRIVE = The value of the FM input, between 0 and 1, offsets the playback position across the whole length of the sample, the FM knob sets the amount of offset.
As well as recording audio signals the sampler can also be used to record, playback and loop 'pitch', 'gate' or 'modulation' signals fed into the block's input (all signals going in and out of the ports in reaktor blocks are just audio rate signals between -1 and 1, so you can generally feed anything into anything. 'Pitch' signals are signals between 0 and 1 where an interval of 0.1 equals 1 octave thus giving a range of 10 octaves between 0 and 1, 'gate' signals are generally just a pulse between 0 and 1 etc).
Piano Roll

A sophisticated PIANO ROLL block with extensive editing and modulation functions. The block includes two automation / modulation lanes. The modulation data from the lanes can be used to modulate, warp and transpose the notes of the piano roll itself in addition to being sent from the A & B modulation outputs. The block features 8 pattern locations, launch quantisation and powerful note and automation editing tools as well as a bank of 16 knobs to modulate pitch, timing, key and scale to warp and stretch the notes and a variety of ways in realtime while the sequence is playing.
Notes can be recorded and played back simultaneously at different positions in the sequence, and the RECORD POSITION, PITCH and GATE ports can be used to 'algorithmically' enter new note sequences by connecting LFOs or modulations sources to these ports.
Features include:
- 16 realtime modulatable knobs for pitch, swing, note length, stretch, warp, scale, key etc
- 8 different patterns that can be re-triggered, twisted, stretched and warped fluidly as they are played
- Launch Quantise feature keeps jamming locked to the beat
- Input ports allow for algorithmic inputting of notes by connecting LFOs and other modulation sources
- Note editing tools match features found on high end DAWs
OSC-Multi Oscillator (Polyphonic)

An polyphonic oscillator that can operate in 5 different modes:
- Supersaw = Old school supersaw oscillator with extra aliasing and grunge.
- Pulse = 2 Pulse oscillators that can be detuned for extra fatness.
- OSC Sync = 2 oscillators the synced together so that one oscillator resets the other oscillator every cycle.
- Ring Mod = 2 oscillators ring-modulated (the outputs multiplied together).
- FM = 2 oscillators configured so that one modulates the phase of the other for dissonant FM sounds.
There are 4 controls (Depth, Pitch, Shape & Option) that have different functions depending on the mode:
Supersaw:
- Depth = Detune
- Pitch = Chord Select
- Shape = FM amount
- Option = Snap notes in chords to scale
Pulse:
- Depth = Oscillator mix
- Pitch = Oscillator 2 pitch
- Shape = Pulse width
- Option = Oscillator 2 square mode
OSC Sync:
- Depth = Oscillator 1 pitch
- Pitch = Oscillator 2 pitch
- Shape = Oscillator shape
- Option = Oscillator 1 Pulse Width
Ring Mod:
- Depth = Dry/wet mix
- Pitch = Oscillator 2 pitch
- Shape = Oscillator shape
- Option = 'Analog' style ring modulation mode
FM:
- Depth = FM Depth
- Pitch = Oscillator 2 Pitch
- Shape = Oscillator shape
- Option = Shape knob controls oscillator 2
Oscillator (Polyphonic)

A simple polyphonic oscillator that can be used either as an audio rate oscillator or as an LFO.
Features a 'Warp' control that bends the waveform in 7 ways:
- BEND+ = Bends the waveform to one side.
- BEND- = Bends the waveform out towards the edges.
- ASYM (Asymmetry) = Squishes the waveform from the middle to the edge in a linear fashion for 'Pulse Width Modulation' style effects.
- SYNC = Duplicates the the waveform a number of times, simulating the 'sync' function found on older analogue synthesisers.
- HYPER = Warps the waveform in an aggressive fashion.
- FOLD (wave-folding) = The waveform acts like a wave-shaper to transform a sine wave. Can be used to create very bright / complex sounds with lots of harmonics.
- WRAP = The waveform is stretched vertically and wrapped back down creating multiple jagged folds.
Features 3 synchronisation modes:
- FREE (wave icon) = The pitch of the oscillator can be set freely with no synchronisation.
- KEY TRACK (keyboard icon) = You can control the pitch of the oscillator via the Pitch input.
- CLOCK (clock Icon) = The speed of the oscillator is synchronised with the master tempo.
Quad Oscillator (Polyphonic)

The oscillator is based on a detailed sampling of a famous polyphonic hardware synth from the 1980s. The samples have been carefully recorded and matched to maintain perfect phase relationships between the 4 oscillators resulting in a very authentic sound.
Note: A positive zero crossing at the 'Reset' port input causes the oscillator to restart. A 'reset' will cause the sampler engine to select a sample with the closest original pitch to the current pitch (set by the signal at the PITCH input as well as the COARSE and FINE pitch knobs). If the reset port isn't connected then the sampler engine will update the selected sample when pitch changes are detected which may result in glitches to be heard when bending notes.
Wavetable (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic wavetable based oscillator. The wavetables can be scanned in 2 dimensions across a 16 by 16 grid with many unique ways of twisting and warping the waveforms.
Wavetable Basic (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic wavetable based oscillator. The oscillator has no built-in wavetables, drag and drop a wavetable file to load it. Use the ‘SELECT’ control to select which of the loaded wavetable files is being used. As well as being able to drag and drop wavetable files you can also load wavetables into Reaktor’s built in sample map editor which will allow you to embed the files into the block.
There is a built in scanning circuit that scans the X position in a variety of ways, the 'SCAN' control sets the depth of the scanning, turn the control to the right for forwards scanning and turn to the left for backwards scanning, double click on the control to reset it to the middle (no scanning). The 'SPEED' control sets the speed of scanning. The following scan modes are available:
- LOOP = The position is scanned in one direction, continuously looping.
- PONG (ping-pong) = The position is scanned in one direction and then reverses, continuously looping forwards and then backwards in a ping-pong fashion.
- ONCE = The position is scanned in one direction and then stops when it reaches the end of its scan.
- ENV = The position is scanned in one direction and then stops, the oscillator is muted by an envelope when the scanner reaches the end. The release speed of the envelope is set on the options page with the ‘RELEASE’ control.
- END = The position is scanned in one direction and then loops only the end part of the scan. This is useful for scanning through wavetables of real instruments so that the beginning / attack portion of the wavetable only plays once and then only the sustain portion is looped.
- RAND (random) = Randomly scans through the wavetable.
- STAG (stagger) = Same as RAND except each voice in unison mode is scanned with different random values, good for very thick unison drone sounds.
The oscillator also features a 'WARP' control that bends the waveform in 1 of 8 ways:
- BEND = Bends the waveform to one side.
- ASYM (Asymmetry) = Squishes the waveform from the middle to the edge in a linear fashion for 'Pulse Width Modulation' style effects.
- SYNC = Duplicates the the waveform a number of times, simulating the 'Sync' function found on older analogue synthesisers.
- HYPER = Warps the waveform in an aggressive fashion.
- FOLD = The waveform acts like a wave-shaper to transform a sine wave. Can be used to create very bright / complex sounds with lots of harmonics.
- FM SELF = Modulates the phase of the oscillator with its own output (FM Feedback similar to feedback found in 'DX' style hardware synths).
- FM 1 = The 7 unison voices are connected together using an FM algorithm similar to one of the algorithms found in a 'DX' style hardware synth. The 'CYCLES / FM RATIO' control offsets the ratio between the carrier and modulator voices.
- FM 2 = The 7 unison voices are connected together using a different FM algorithm similar to an algorithm found in a 'DX' style hardware synth. The 'CYCLES / FM RATIO' control offsets the ratio between the carrier and modulator voices.
'CYCLES / FM RATIO' control: when this control is set to a value greater than 1 the warping is only applied to one cycle in a series of waveform cycles and the remaining cycles are not warped. If one of the FM warp modes is selected then this control changes the ratio between the carrier and modulator voices.
The 'HARM' (harmonic) control uses chebyshev filters to boost or cut particular harmonics in the waveform and change its tonal character. The order of the chebyshev filters can be set on the options page using the ‘ORDER’ control.
Comb Notch Filter (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic comb and notch filter with a 'zero feedback delay' design (a more accurate way of modelling the feedback path of an analog filter where no delay is introduced to the feedback path). The filter produces a rich resonant sound and it can be used for physical modelling style synthesis to emulate drum skins, resonant tubes or strings. 4 filter modes are available:
- COMB = Comb filter, 'DAMP' control sets the damping (reducing of high frequencies) in the feedback path.
- NOTCH X2 = Notch filter with 2 notches. 'SPREAD' control sets the distance between the notches.
- NOTCH X4 = Notch filter with 4 notches.
- NOTCH X6 = Notch filter with 6 notches
The filter features pre or post filter saturation with 5 styles of distortion:
- SAT = low aliasing simulation of analog saturation.
- SINE = sine-wave shaped 'wave-folding' distortion with lots of tone.
- SINE X10 = extreme 'wave-folding' style distortion.
- KINKY = triangle shaped wave-folding.
- DRIVE = low aliasing simulation of an overdrive pedal.
- ATAN = A simple saturation curve.
- CLIP = hard clipping.
Turning the distortion control to the left increases pre-filter distortion, turning it to the right increases post-filter distortion. When the distortion control is set in the central position the saturation stage is bypassed.
The block features a built in 'exciter' that, when triggered produces a short burst of sound that excites and resonates the filters. There are controls on the options page for the exciter's tone and envelope as well as a setting for internal saturation / drive levels.
Filter (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic filter with a 'zero feedback delay' design (a more accurate way of modelling the feedback path of an analog filter where no delay is introduced to the feedback path).
The filter features pre or post filter saturation with 7 styles of distortion:
- SAT = low aliasing simulation of analog saturation.
- SINE = sine-wave shaped 'wave-folding' distortion with lots of tone.
- SINE X10 = extreme 'wave-folding' style distortion.
- KINKY = triangle shaped wave-folding.
- DRIVE = low aliasing simulation of an overdrive pedal.
- ATAN = A simple saturation curve.
- CLIP = hard clipping.
Turning the distortion control to the left increases pre-filter distortion, turning it to the right increases post-filter distortion. When the distortion control is set in the central position the saturation stage is bypassed.
Includes mono and stereo versions. The stereo version has a 'STEREO A/B MODULATION' switch on the 'Options' panel. When this is enabled the A/B modulation is split up: A only affects the left channel and B only affect the right channel allowing independent modulation of each channel.
Mini Filter (Polyphonic)

A simple polyphonic filter using a low CPU 'zero feedback delay' design (a more accurate way of modelling the feedback path of an analog filter where no delay is introduced to the feedback path).
Envelope (Polyphonic)

A versatile polyphonic ADSR (attack, decay, sustain release) style envelope with individual shape controls for each stage. The cycle switch causes the the envelope to cycle back to the start, making it behave like an LFO or oscillator. When the hold switch is enabled the envelope stays open until all stages have finished and note offs are ignored. The envelope also features controls on the options page to set the start and end level for the attack stage for more flexibility. The 'In' and 'Out' ports are connected to an amplifier inside the block that is controlled by the envelope so it isn't necessary to use a separate VCA (voltage controlled amplifier) to control signals.
Multi-Breakpoint Envelope (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic multi-breakpoint envelope with up to 50 breakpoints. The envelope shapes can be stored into 8 presets which can be selected manually on the GUI, by using the modulation inputs or via MIDI. There is also a ‘Round-Robin’ option which will cause the envelope to cycle through the presets with every gate received. Right click on the presets numbers to copy and paste between presets. Right click and then click and drag to copy and then paste across multiple presets numbers. The depth control allows the envelope to be scaled or inverted.
The breakpoints (circles), shape-points (small squares) and the loop markers can be moved by clicking on the objects and dragging them. A new breakpoint is inserted by a right click at the desired position. A right click on a breakpoint deletes it.
The loop start and loop end markers can be moved by dragging them between breakpoints. If the loop is active the envelope will loop continuously while the the signal at the 'GATE' port is positive, after which the envelope will continue on to the end.
To simultaneously scroll the envelope and to set the zoom factor click on the background of the envelope. Dragging to the left or right scrolls the envelope, dragging up zooms out and dragging down zooms in. The ruler can be used to shift and to zoom independently, left button click and drag on the ruler to scroll, right click and drag to zoom. The zoom factor defines the grid size of the ruler markings.
A double-click sets the zoom factor so that the whole envelope fits on the display.
There is a control on the options page to enable MIDI control, allowing the presets to be switched by a range of MIDI notes on a hardware MIDI controller.
Randomizer (Polyphonic)

4 channel polyphonic random value generator.
Generates a random value at the output every time a gate signal is received. Values can change instantly or ramp between values, transition time between values is set by the slope control.
Unison (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic unison / detune effect. The RESET input resets the detuning of the audio. A gate signal must be connected to this port for the effect to be heard correctly.
Real Verb

A high quality, realistic reverb effect with a choice of early reflection patterns. The 'DIFF' (diffusion) control sets the smoothness and density of the tail. There are also controls to reduce sample rate, bit depth and increase saturation for gritty, vintage digital reverb effects.
Box Verb

A reverb effect used to simulate boxes, containers and small spaces.
4 Ch Mixer (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic 4 channel mixer. The mixer has 8 modes with which it uses to mix the channels (the mixing mode is applied to channels 1+2 & 3+4 as 2 separate groups of channels):
There are 8 different modes for the mixer:
- MIX = Normal Mixer.
- RING A = Analog Ring Modulation. Level control 2/4 functions as a dry/wet control.
- RING D = Digital Ring Modulation. Level control 2/4 functions as a dry/wet control.
- AM A = Analog Amplitude Modulation.
- AM D = Digital Amplitude Modulation.
- S&H = Sample & Hold Method 1 (Hold when input 2/4 crosses zero). Level control 2/4 functions as a dry/wet control.
- HOLD = Sample & Hold Method 2 (Hold when input 2/4 is positive, pass when input 2/4 is negative). Level control 2/4 functions as a dry/wet control.
- OR = Selects the signal with the most positive amplitude.
If the individual channel outputs are connected but the channel inputs are disconnected then the outputs will send out a constant value equivalent to the setting of the level control, enabling the level control to be used as a 'macro' control.
Dual VCA Mixer (Polyphonic)

2 polyphonic VCAs (Voltage Controlled Amplifiers) with controls for depth and modulation shape.
The VCA has 8 modes with which it uses to mix the 2 channels before sending them to the 'MIX' output:
- MIX = Normal Mixer.
- RING A = Analog Ring Modulation.
- RING D = Digital Ring Modulation.
- AM A = Analog Amplitude Modulation.
- AM D = Digital Amplitude Modulation.
- S&H = Sample & Hold Method 1 (Hold when input 2 crosses zero).
- HOLD = Sample & Hold Method 2 (Hold when input 2 is positive, pass when input 2 is negative).
- OR = Selects the signal with the most positive amplitude.
Mono Note Merge (Polyphonic)

Merges mono pitch and gate signals together and outputs the merged notes to a pair of polyphonic pitch and gate ports. Click on the LEDs to mute each channel.
Mono To Voice

Each row connects to a single voice of the polyphonic output. Row 1 to voice 1, row 2 to voice 2, row 3 to voice 3 etc.
Multiply (Polyphonic)

Each polyphonic input port in a row is multiplied with its neighbour. If ports are un-connected they are ignored.
Note To Gate

Creates gate signals from a polyphonic signals.
Poly Note Merge (Polyphonic)

Merges polyphonic pitch and gate signals together and outputs the merged notes to a pair of polyphonic pitch and gate ports. Click on the LEDs to mute each channel.
Poly To Mono

Each polyphonic input port in a row is summed with its neighbour then the voices are summed to the monophonic output.
Poly Voice Split

Notes arriving at the polyphonic PITCH and GATE ports are sorted according to the state of the LO-HI button and then sent out to the 3 pairs of monophonic PITCH and GATE output ports. The polyphony of the output signal is determined by which output ports are connected: if only PITCH 1 and GATE 1 is connected then the output will be monophonic, if PITCH 1 and GATE 1 and PITCH 2 and GATE 2 are connected then the output will be 2 note polyphonic, if all 6 output ports are connected then the output will be 3 note polyphonic.
Short Delay (Polyphonic)

A 4 channel delay block.
MODE
HQ = Delay with high quality interpolation. Good for modulating the delay control. Delay time in milliseconds
BASIC = Delay with no interpolation. Delayed signal is identical to the input signal.
SAMPLE = Delay with no interpolation. Delay time in samples.
If an input port is not connected then INPUT 1 will be used by default.
Sum (Polyphonic)

Each polyphonic input port in a row is summed with its neighbour. If ports are un-connected they are ignored.
Util Note In (Polyphonic).ism

A polyphonic note in block.
Chord Bank (Polyphonic)

A block that stores a bank of 120 chords (each with up to 6 notes). The chords can be selected using the PITCH input or triggered using the PITCH and GATE inputs together.
Clock Multiplier

A 4 channel clock multiplier. The block automatically inserts a number of clocks in between each clock arriving at the inputs for each channel. Perfect for creating complex polyrhythmic patterns from a simple clock input.
Gate Probability

Thins out gates arriving at the gate inputs. The probability of gates being passed by each channel is set by value of the PROBABILITY knobs in %. The block operates in 4 modes:
MODE 1 = Each channel operates independently.
MODE 2 = Channel 1 is sent to either output 1 or 2, channel 3 is sent to either output 3 or 4.
MODE 3 = Channels 1, 2 & 3 are cascaded (channel 1 is sent to either output 1 or feeds channel 2, channel 2 is sent to either output 2 or feeds channel 3), channel 4 is independent.
MODE 4 = Channels 1, 2, 3 & 4 are cascaded.
Quantize

Quantizes the input signal by the value of the STEPS knob.
Sequential Switch - An 8 input, 8 output switch. The connections between input 1 and the 8 outputs or between the 8 inputs and output 1 are switched using a sequencer. The position of the sequencer is incremented by gates received at the GATE input. (Note: this block will also be added to the upcoming V1.2 Free Pack update.) This is an extremely versatile and powerful block that can be used in may ways to combine, split and splice gate and audio signals.
Split

Splits incoming notes between 3 sets of pitch and gate outputs using 3 different modes: NOTE, VELOCITY & MIX.
Transpose (Polyphonic)

Transposes polyphonic pitch signals. A scale button applies pitch snapping to the output.
Voice Split

Each voice of the polyphonic input is sent to a different monophonic output.
Keyboard

A dual keyboard display that can also be used to trigger or perform notes with the mouse.
MIDI Out (Polyphonic)

Converts polyphonic pitch and gate signals to MIDI notes and also offers four channels of MIDI CC output.
Mono Note Merge (Polyphonic)

Merges mono pitch and gate signals together and outputs the merged notes to a pair of polyphonic pitch and gate ports. Click on the LEDs to mute each channel.
Mutes X8

A bank of 8 mute buttons.
Note Delay (Polyphonic)
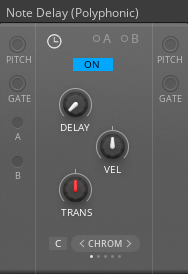
Delays the polyphonic signals arriving at the 'Pitch' and 'Gate' inputs. The block has controls for transposing the pitch of the delayed notes and snapping the pitches to a scale.
Note In (Polyphonic)

A polyphonic MIDI input block.
Gate Merge

Merges gate signals together. If a gate signal is already positive at one port when a new gate arrives at another port then the output will momentarily drop to zero triggering a fresh gate at the output. Includes a new SUM mode, when enabled the gates are added together rather than merged resulting in a higher output when multiple gates arrive at the same time.
